Introduction to XGBoostModel
Overview:
The XGBoostModel module in ADS provides different ways of serializing a trained XGBoost model. This example demonstrates how to use the XGBoostModel module to prepare model artifacts, save models to the model catalog, and deploy any unsupported model framework.
A model artifact includes the model, metadata about the model, input and output schema, and a script to load the model and make predictions. You can share model artifacts among data scientists, track for provenance, reproduce, and deploy.
Initialize
XGBoostModel() initiates an XGBoost model instance and accepts the following variables:
estimator: (Callable). Trained XGBoost model either using learning API or sklearn API.artifact_dir: str. Artifact directory to store the files needed for deployment.properties: (ModelProperties, optional). Defaults to None. TheModelPropertiesobject is required to save and deploy models.auth :(Dict, optional). Defaults to None. The default authentication is set usingads.set_authAPI. If you need to override the default, useads.common.auth.api_keysorads.common.auth.resource_principalto create appropriate authentication signer and kwargs required to instantiateIdentityClientobject.
The score.py file is automatically generated and you don’t have to modify it though you can change its contents. For example, you could add your preferred steps to pre_inference and post_inference.
The properties instance of ModelProperties has the following predefined fields:
inference_conda_env: strinference_python_version: strtraining_conda_env: strtraining_python_version: strtraining_resource_id: strtraining_script_path: strtraining_id: strcompartment_id: strproject_id: strdeployment_instance_shape: strdeployment_instance_count: intdeployment_bandwidth_mbps: intdeployment_log_group_id: strdeployment_access_log_id: strdeployment_predict_log_id: str
By default,
propertiesis populated from environment variables if it’s not specified. For example in a notebook session, by default the environment variables for project id and compartment id are preset, and stored inPROJECT_OCIDandNB_SESSION_COMPARTMENT_OCID. Thepropertiesinstance populates those variables from the environment variables, and uses those values in functions like.save()and.deployment()by default. However, you can always explicitly pass the variables into the functions to overwrite the values. For the fields thatpropertieshas, it records the values that you pass into the functions. For example, when you passinference_conda_envinto.prepare(), thenpropertiesrecords this value, and later you can export it using.to_yaml(). Then reload it using.from_yaml()from any machine. This way, you can reuse the properties in different places.
Summary_status
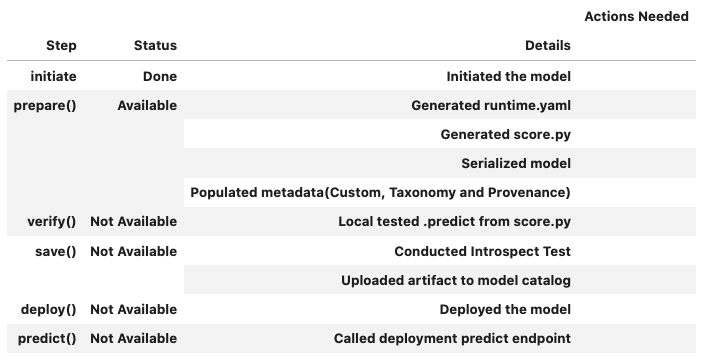
You can call the``.summary_status()`` function any time after the XGBoostModel instance is created.
An example of a summary status table looks is similar to the following after you initiate the model instance. The step column shows all the functions. It shows that the initiate step is completed where the Details column explained that what initiate step did. Now, prepare() is available. The next step is to call prepare().
Prepare
The .prepare() function takes the following parameters:
inference_conda_env: (str, optional). Defaults to None. Can be either slug or the Object Storage path of the conda environment. You can only pass in slugs if the conda environment is a service environment.inference_python_version: (str, optional). Defaults to None. Python version to use to deploy.training_conda_env: (str, optional). Defaults to None. Can be either slug or the Object Storage path of the conda environment. You can only pass in slugs if the conda environment is a service environment.training_python_version: (str, optional). Defaults to None. Python version used during training.model_file_name: (str). Name of the serialized model.as_onnx: (bool, optional). Defaults to False. Whether to serialize as an ONNX model.initial_types: (List[Tuple], optional). Defaults to None. Each element is a tuple of a variable name and a type, see ONNX examples.force_overwrite: (bool, optional). Defaults to False. Whether to overwrite existing files.namespace: (str, optional). Namespace of region. This is used for identifying which region the service environment is from when you pass a slug toinference_conda_envandtraining_conda_env.use_case_type: str. The use case type of the model. Use it withUserCaseTypeclass or string provided inUseCaseType. For example,use_case_type=UseCaseType.BINARY_CLASSIFICATIONoruse_case_type="binary_classification". Review theUseCaseTypeclass to see all supported types.X_sample: Union[Dict, str, List, np.ndarray, pd.core.series.Series, pd.core.frame.DataFrame,]. Defaults to None.y_sample: Union[Dict, str, List, pd.Series, np.ndarray]. Defaults to None. A sample of output data for use to generate output schema.training_script_path: str. Defaults to None. Training script path.training_id: (str, optional). Defaults to value from environment variables. The training OCID for model. It can be notebook session or job OCID.ignore_pending_changes: bool. Defaults to False. Whether to ignore the pending changes in Git.max_col_num: (int, optional). Defaults toutils.DATA_SCHEMA_MAX_COL_NUM. The maximum column size of the data that allows you to automatically generate a schema.
kwargs:
impute_values: (dict, optional). The dictionary where the key is the column index (or names is accepted for Pandas dataframe), and the value is the impute value for the corresponding column.
Note:
1. We provide two ways of serializing the models: local method which is supported by xgboost and onnx method. By default, local method is used and also it is recommended way of serialize the model.
2. prepare() also takes any variables that skl2onnx.convert_sklearn takes when the estimator is using the sklearn API. If the estimator is using the learning API, then kwargs takes variables that onnxmltools.convert_xgboost takes.
It automatically generates the following files.
runtime.yamlscore.pymodel.jsonDefault name. Ifas_onnx=True, then the default file name should bemodel.onnx. However, you can set model file name.input_schema.jsonWhenX_sampleis passed in and the schema is more than 32kb.output_schema.jsonWheny_sampleis passed in and the schema is more than 32kb.hyperparameters.jsonIf extracted hyperparameters is more than 32kb.
Verify
The .verify() function takes one parameter:
data (Union[Dict, str, List, np.ndarray, pd.core.series.Series, pd.core.frame.DataFrame]). Data used to test if deployment works in your local environment.
You use this function to test whether the deployment works in the local environment. Before saving and deploying the model, we recommended that you call this function to check if load_model and predict functions in score.py works. It takes and returns the same data as the model deployment predict takes and returns.
In XGBoostModel, data serialization is supported for dictionary, string, list, np.ndarray, pd.core.series.Series, and pd.core.frame.DataFrame. It means that you can pass in a Pandas dataframe or Numpy array even though they are not JSON serializable because the data is automatically serialized and deserialized.
Save
The .save() function takes the following parameters:
display_name: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The name of the model.description: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The description of the model.freeform_tags : Dict(str, str). Defaults to None. Free form tags for the model.defined_tags : (Dict(str, dict(str, object)), optional). Defaults to None. Defined tags for the model.ignore_introspection: (bool, optional). Defaults to None. Determines whether to ignore the result of the model introspection or not. If set to True, thensave()ignores all model introspection errors.
kwargs:
project_id: (str, optional). Project OCID. If not specified, the value is taken either from the environment variables or the model properties.compartment_id : (str, optional). Compartment OCID. If not specified, the value is taken either from the environment variables or the model properties.timeout: (int, optional). Defaults to 10 seconds. The connection timeout in seconds for the client.
It first reloads the score.py and runtime.yaml files from disk so that any changes made to those files can be picked up. Then it conducts an introspection test by default. However, you can set ignore_introspection=False to avoid it. The introspection test checks if .deployment() could have some issues and suggests any necessary actions needed so that you can fix them. Lastly, it will upload the artifacts to the model catalog and return a model_id for the saved model.
You can also call .instrospect() to conduct the test any time after .prepare() is called.
Deploy
.deploy() takes the following parameters:
wait_for_completion : (bool, optional). Defaults to True. Flag set to wait for deployment to complete before proceeding.display_name: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The name of the model.description: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The description of the model.deployment_instance_shape: (str, optional). Defaults toVM.Standard2.1. The shape of the instance used for deployment.deployment_instance_count: (int, optional). Defaults to 1. The number of instance used for deployment.deployment_bandwidth_mbps: (int, optional). Defaults to 10. The bandwidth limit on the load balancer in Mbps.deployment_log_group_id: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The OCI logging group id. The access log and predict log share the same log group.deployment_access_log_id: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The access log OCID for the access logs, see loggingdeployment_predict_log_id: (str, optional). Defaults to None. The predict log OCID for the predict logs, see logging
kwargs:
project_id: (str, optional). Project OCID. If not specified, the value is taken from the environment variables.compartment_id : (str, optional). Compartment OCID. If not specified, the value is taken from the environment variables.max_wait_time : (int, optional). Defaults to 1200 seconds. Maximum amount of time to wait in seconds. Negative implies infinite wait time.poll_interval : (int, optional). Defaults to 60 seconds. Poll interval in seconds.
This function deploys the model. In order to make deployment more smooth, we suggest using exactly the same conda environments for both local development and deployment. Discrepancy between the two could cause problems.
You can pass in deployment_log_group_id, deployment_access_log_id and deployment_predict_log_id to enable the logging. Please refer to this logging example for an example on logging. To create a log group, you can reference Logging session.
Predict
The .predict() function takes one parameter, Data, expected by the predict API in score.py.
- data (Union[Dict, str, List, np.ndarray, pd.core.series.Series, pd.core.frame.DataFrame]).
.predict() takes the same data that .verify() takes so ensure the data passed and returned by predict in the score.py is JSON serializable. It passes the data to the model deployment endpoint and calls the predict function in the score.py.
Delete_deployment
The .delete_deployment() function takes one parameter:
wait_for_completion: (bool, optional). Defaults to False. Whether to wait until completion.
If you don’t need the deployment any longer, you can call delete_deployment to delete the current deployment that is attached to this model. Each time you call deploy, it creates a new deployment ,and only the new deployment is attached to the model.
from_model_artifact
.from_model_artifact() allows to load a model from a folder, zip or tar achive files, where the folder/zip/tar files should contain the files such as runtime.yaml, score.py, the serialized model file needed for deployments. It takes the following parameters:
uri: str: The folder path, ZIP file path, or TAR file path. It could contain a seriliazed model(required) as well as any files needed for deployment including: serialized model, runtime.yaml, score.py and etc. The content of the folder will be copied to theartifact_dirfolder.model_file_name: str: The serialized model file name.artifact_dir: str: The artifact directory to store the files needed for deployment.auth: (Dict, optional): Defaults to None. The default authetication is set usingads.set_authAPI. If you need to override the default, use the ads.common.auth.api_keys or ads.common.auth.resource_principal to create appropriate authentication signer and kwargs required to instantiate IdentityClient object.force_overwrite: (bool, optional): Defaults to False. Whether to overwrite existing files or not.properties: (ModelProperties, optional): Defaults to None. ModelProperties object required to save and deploy model.
After this is called, you can call .verify(), .save() and etc.
from_model_catalog
from_model_catalog allows to load a remote model from model catalog using a model id , which should contain the files such as runtime.yaml, score.py, the serialized model file needed for deployments. It takes the following parameters:
model_id: str. The model OCID.model_file_name: (str). The name of the serialized model.artifact_dir: str. The artifact directory to store the files needed for deployment. Will be created if not exists.auth: (Dict, optional). Defaults to None. The default authetication is set usingads.set_authAPI. If you need to override the default, use theads.common.auth.api_keysorads.common.auth.resource_principalto create appropriate authentication signer and kwargs required to instantiate IdentityClient object.force_overwrite: (bool, optional). Defaults to False. Whether to overwrite existing files or not.properties: (ModelProperties, optional). Defaults to None. ModelProperties object required to save and deploy model.
kwargs:
compartment_id : (str, optional). Compartment OCID. If not specified, the value will be taken from the environment variables.timeout : (int, optional). Defaults to 10 seconds. The connection timeout in seconds for the client.
Examples
Create a XGBoost Estimator
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import tempfile
import warnings
import xgboost as xgb
from ads.catalog.model import ModelCatalog
from ads.model.framework.xgboost_model import XGBoostModel
from shutil import rmtree
from skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorType
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OrdinalEncoder
# Load data. You can download the data from this link. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/bank+marketing
df_path = os.path.join("/", "opt", "notebooks", "ads-examples", "oracle_data", "orcl_attrition.csv")
df = pd.read_csv(df_path)
y = df["Attrition"]
X = df.drop(columns=["Attrition"])
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)
# Label encode the y values
le = LabelEncoder()
y_train_transformed = le.fit_transform(y_train)
y_test_transformed = le.transform(y_test)
# Extract numerical columns and categorical columns
categorical_cols = []
numerical_cols = []
for i, col in X.iteritems():
if col.dtypes == "object":
categorical_cols.append(col.name)
else:
numerical_cols.append(col.name)
categorical_transformer = Pipeline(
steps=[
('encoder', OrdinalEncoder(handle_unknown="use_encoded_value", unknown_value=-999))
]
)
# Build a pipeline
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
('cat', categorical_transformer, categorical_cols)
]
)
preprocessor_pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor)])
preprocessor_pipeline.fit(X_train)
X_train_transformed = preprocessor_pipeline.transform(X_train)
X_test_transformed = preprocessor_pipeline.transform(X_test)
# XGBoost Learning API
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train_transformed, y_train_transformed)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test_transformed, y_test_transformed)
estimator_learn = xgb.train(
params = {"learning_rate": 0.01, "max_depth": 3},
dtrain = dtrain,
)
# XGBoost Scikit-Learn API
estimator = xgb.XGBClassifier(
n_estimators=100, learning_rate=0.01, random_state=42
)
estimator.fit(
X_train_transformed,
y_train_transformed,
)
XGBoost Framework Serialization - Learning API
learning_api_model = XGBoostModel(estimator=estimator_learn, artifact_dir=tempfile.mkdtemp())
learning_api_model.prepare(
inference_conda_env="generalml_p37_cpu_v1",
force_overwrite=True,
)
learning_api_model.verify(X_test_transformed[:10])['prediction']
learning_api_model.save()
learning_api_model.deploy()
learning_api_model.predict(X_test_transformed[:10])['prediction']
learning_api_model.delete_deployment()
XGBoost Framework Serialization - Sklearn API
sklearn_api_model = XGBoostModel(estimator=estimator, artifact_dir=tempfile.mkdtemp())
sklearn_api_model.prepare(
inference_conda_env="generalml_p37_cpu_v1",
force_overwrite=True,
)
sklearn_api_model.verify(X_test_transformed[:10])['prediction']
sklearn_api_model.save()
sklearn_api_model.deploy()
sklearn_api_model.predict(X_test_transformed[:10])['prediction']
sklearn_api_model.delete_deployment()
XGBoost Onnx Serialization - Learning API
learning_api_model_onnx = XGBoostModel(estimator=estimator_learn, artifact_dir=tempfile.mkdtemp())
initial_types = [('input', FloatTensorType(shape=[None, 8]))]
learning_api_model_onnx.prepare(
inference_conda_env="oci://bucket@namespace/path/to/custom_conda_pack",
inference_python_version="3.7",
as_onnx=True,
force_overwrite=True,
initial_types=initial_types,
)
learning_api_model_onnx.verify(X_test_transformed[:10].astype("float32"))['prediction']
learning_api_model_onnx.save()
learning_api_model_onnx.deploy()
learning_api_model_onnx.predict(X_test_transformed[:10].astype("float32"))['prediction']
learning_api_model_onnx.delete_deployment()
XGBoost Onnx Serialization - Sklearn API
sklearn_api_model_onnx = XGBoostModel(estimator=estimator, artifact_dir=tempfile.mkdtemp())
initial_types = [('input', FloatTensorType(shape=[None, 8]))]
sklearn_api_model_onnx.prepare(
inference_conda_env="oci://bucket@namespace/path/to/custom_conda_pack",
inference_python_version="3.7",
as_onnx=True,
force_overwrite=True,
initial_types=initial_types,
)
sklearn_api_model_onnx.verify(X_test_transformed[:10].astype("float32"))['prediction']
sklearn_api_model_onnx.save()
sklearn_api_model_onnx.deploy(wait_for_completion=False)
sklearn_api_model_onnx.predict(X_test_transformed[:10].astype("float32"))['prediction']
sklearn_api_model_onnx.delete_deployment()
Loading Model From a Zip Archive
model = XGBoostModel.from_model_artifact("/folder_to_your/artifact.zip",
model_file_name="your_model_file_name",
artifact_dir=tempfile.mkdtemp())
model.verify(your_data)
Loading Model From Model Catalog
model = XGBoostModel.from_model_catalog(model_id="ocid1.datasciencemodel.oc1.iad.amaaaa....",
model_file_name="your_model_file_name",
artifact_dir=tempfile.mkdtemp())
model.verify(your_data)